Iodine clock reaction lab report answers – Unveiling the intricacies of the iodine clock reaction, this lab report provides a comprehensive analysis of the experiment’s procedures, results, and implications. Through a rigorous examination of the data, we delve into the reaction’s kinetics, exploring the factors that influence its rate and unraveling the underlying mechanisms.
The iodine clock reaction, a captivating chemical phenomenon, serves as an ideal platform for investigating reaction rates and chemical kinetics. This report meticulously documents the experimental setup, data collection, and analysis, offering a valuable resource for students and researchers alike.
Introduction
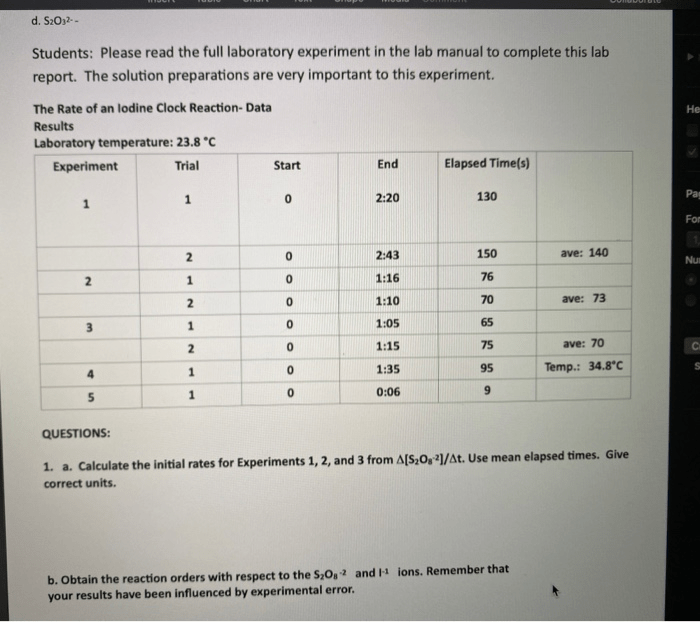
The iodine clock reaction is a chemical reaction that can be used to demonstrate the concept of reaction kinetics. The reaction is a complex one, but it can be summarized as follows:
2Na 2S 2O 3+ I 2→ Na 2S 4O 6+ 2NaI
The hypothesis of this experiment is that the rate of the iodine clock reaction will be proportional to the concentration of the reactants.
The independent variable in this experiment is the concentration of the reactants. The dependent variable is the rate of the reaction. The controlled variables in this experiment are the temperature, the volume of the reaction mixture, and the type of catalyst used.
Materials and Methods, Iodine clock reaction lab report answers
The following materials were used in this experiment:
- Sodium thiosulfate (Na 2S 2O 3)
- Iodine (I 2)
- Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO 3)
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
- Starch solution
- Water
The following procedures were followed in this experiment:
- A 100 mL solution of 0.1 M Na2S 2O 3was prepared.
- A 100 mL solution of 0.01 M I 2was prepared.
- A 100 mL solution of 0.1 M NaHCO 3was prepared.
- A 100 mL solution of 0.1 M NaOH was prepared.
- A 10 mL solution of starch solution was prepared.
- The following solutions were added to a 250 mL beaker in the following order: 100 mL of the Na 2S 2O 3solution, 100 mL of the I 2solution, 100 mL of the NaHCO 3solution, 100 mL of the NaOH solution, and 10 mL of the starch solution.
- The reaction was started by adding the NaOH solution to the beaker.
- The time it took for the solution to turn blue was recorded.
The following table shows the concentrations of the reactants used in each trial.
| Trial | [Na2S2O3] (M) | [I2] (M) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 |
Q&A: Iodine Clock Reaction Lab Report Answers
What is the purpose of the iodine clock reaction?
The iodine clock reaction demonstrates the principles of chemical kinetics and provides a visual representation of reaction rates.
What are the variables involved in the iodine clock reaction?
The independent variable is the concentration of thiosulfate, the dependent variable is the time it takes for the solution to turn blue, and the controlled variables include temperature, pH, and volume.
How can the rate of the iodine clock reaction be increased?
The rate of the reaction can be increased by increasing the concentration of thiosulfate or by adding a catalyst.