The human menstrual cycle lab 31 answer key – The Human Menstrual Cycle: Lab 31 Answer Key delves into the intricacies of the female reproductive system, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding the menstrual cycle. This detailed resource unravels the physiological processes that govern this essential biological function, empowering individuals with knowledge and fostering a deeper appreciation for their bodies.
Through a meticulous exploration of the menstrual cycle’s phases, hormonal fluctuations, and practical laboratory exercises, this answer key illuminates the complexities of this fundamental aspect of women’s health. By deciphering the intricacies of the menstrual cycle, individuals gain invaluable insights into their reproductive health, empowering them to make informed decisions and navigate this pivotal stage of life with confidence.
The Human Menstrual Cycle
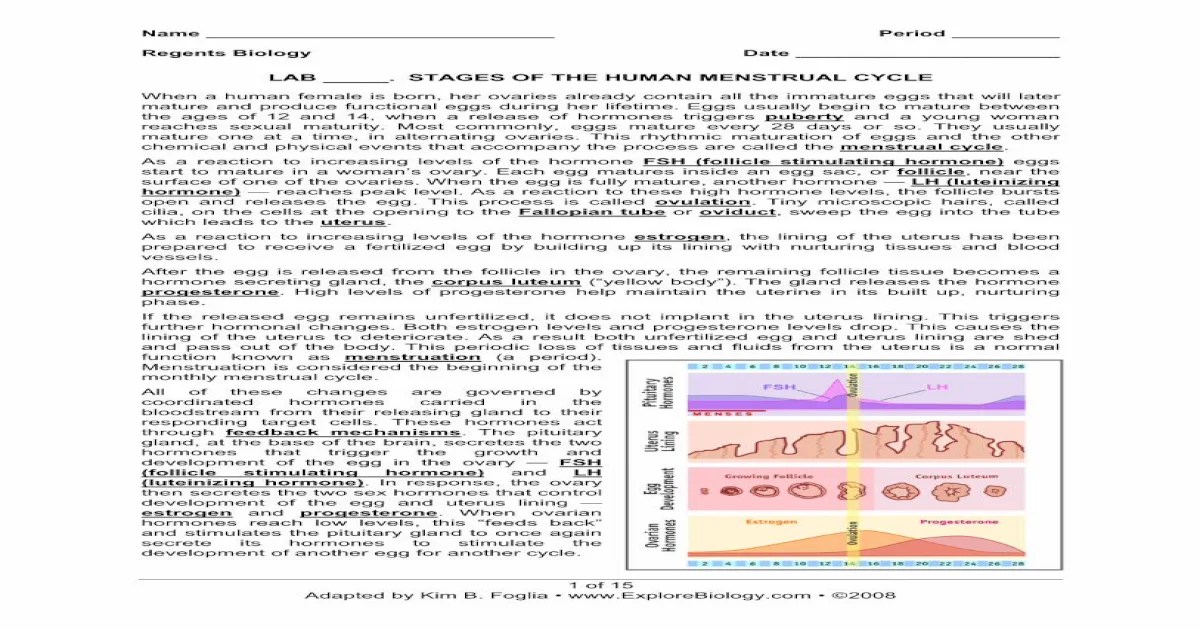
The menstrual cycle is a monthly series of changes that occur in the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The cycle is controlled by hormones, and it typically lasts for 28 days, although it can vary from 21 to 35 days.
The menstrual cycle is divided into four phases: the menstrual phase, the follicular phase, the ovulatory phase, and the luteal phase. The menstrual phase is the first day of bleeding, and it lasts for about 5 days. The follicular phase begins on the first day of bleeding and ends when ovulation occurs.
During the follicular phase, the ovaries produce estrogen, which causes the uterine lining to thicken. The ovulatory phase begins when an egg is released from one of the ovaries. The luteal phase begins after ovulation and ends when the menstrual period begins.
During the luteal phase, the corpus luteum, which is a small gland that forms on the ovary after ovulation, produces progesterone, which helps to maintain the uterine lining.
Hormonal Changes During the Menstrual Cycle, The human menstrual cycle lab 31 answer key
The menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones, including estrogen, progesterone, and luteinizing hormone (LH). Estrogen is produced by the ovaries, and it causes the uterine lining to thicken. Progesterone is also produced by the ovaries, and it helps to maintain the uterine lining.
LH is produced by the pituitary gland, and it causes ovulation to occur.
Lab 31: The Human Menstrual Cycle
Lab 31 is a laboratory exercise that allows students to learn about the human menstrual cycle. The purpose of the lab is to:
- Identify the different phases of the menstrual cycle.
- Understand the hormonal changes that occur during the menstrual cycle.
- Correlate the changes in the uterine lining with the changes in hormone levels.
The materials used in Lab 31 include:
- A microscope
- Slides
- Coverslips
- Uterine tissue samples
- Hormone assay kits
The step-by-step guide to completing Lab 31 is as follows:
- Prepare uterine tissue samples.
- Examine the uterine tissue samples under a microscope.
- Identify the different phases of the menstrual cycle.
- Measure the thickness of the uterine lining.
- Determine the levels of estrogen and progesterone in the blood.
- Correlate the changes in the uterine lining with the changes in hormone levels.
Answer Key for Lab 31
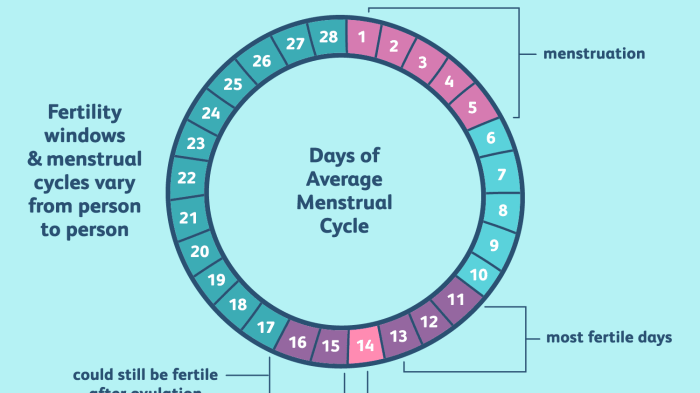
The answers to the questions in Lab 31 are as follows:
- The different phases of the menstrual cycle are the menstrual phase, the follicular phase, the ovulatory phase, and the luteal phase.
- The hormonal changes that occur during the menstrual cycle are:
- Estrogen levels are high during the follicular phase and low during the luteal phase.
- Progesterone levels are low during the follicular phase and high during the luteal phase.
- LH levels are high during the ovulatory phase.
- The changes in the uterine lining are:
- The uterine lining is thin during the menstrual phase.
- The uterine lining thickens during the follicular phase.
- The uterine lining is thickest during the ovulatory phase.
- The uterine lining thins during the luteal phase.
The implications of the results of Lab 31 are that the menstrual cycle is a complex process that is controlled by hormones. The changes in the uterine lining are correlated with the changes in hormone levels. This information can be used to understand the menstrual cycle and to diagnose and treat menstrual disorders.
Further Reading: The Human Menstrual Cycle Lab 31 Answer Key
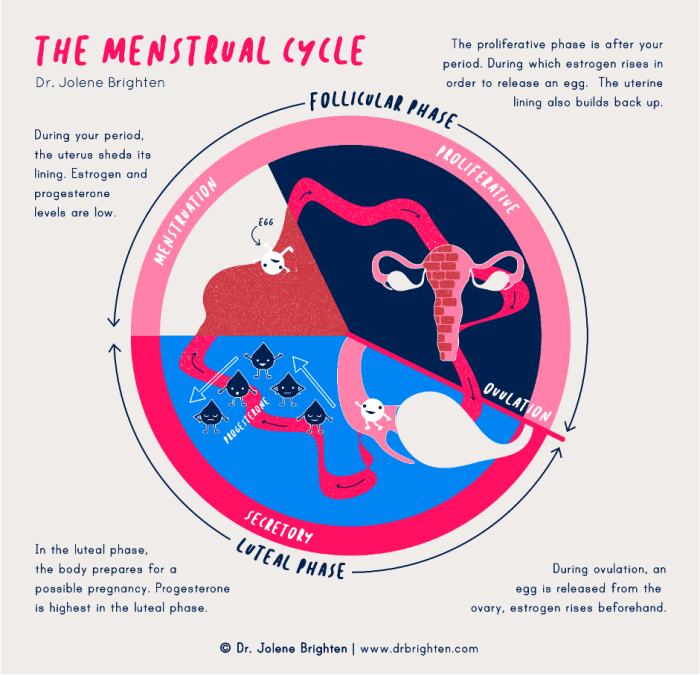
The following resources provide further reading on the human menstrual cycle:
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists: https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/menstrual-cycle
- The National Institutes of Health: https://www.nichd.nih.gov/health/topics/menstrualcycle/conditioninfo/Pages/default.aspx
- The Mayo Clinic: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/menstrual-cycle/symptoms-causes/syc-20374845
Understanding the menstrual cycle is important for women’s health. The menstrual cycle can affect a woman’s physical and emotional health, and it can also be a sign of underlying health problems. By understanding the menstrual cycle, women can make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
Detailed FAQs
What is the purpose of Lab 31?
Lab 31 aims to provide a hands-on learning experience, allowing students to observe and analyze the menstrual cycle’s different phases.
What materials are used in Lab 31?
Lab 31 typically utilizes materials such as menstrual cycle charts, hormone test kits, and microscopes to facilitate observations and data collection.
What are the implications of the results of Lab 31?
The results of Lab 31 can provide insights into the student’s menstrual cycle patterns, hormonal levels, and potential reproductive health concerns, fostering a better understanding of their overall health.